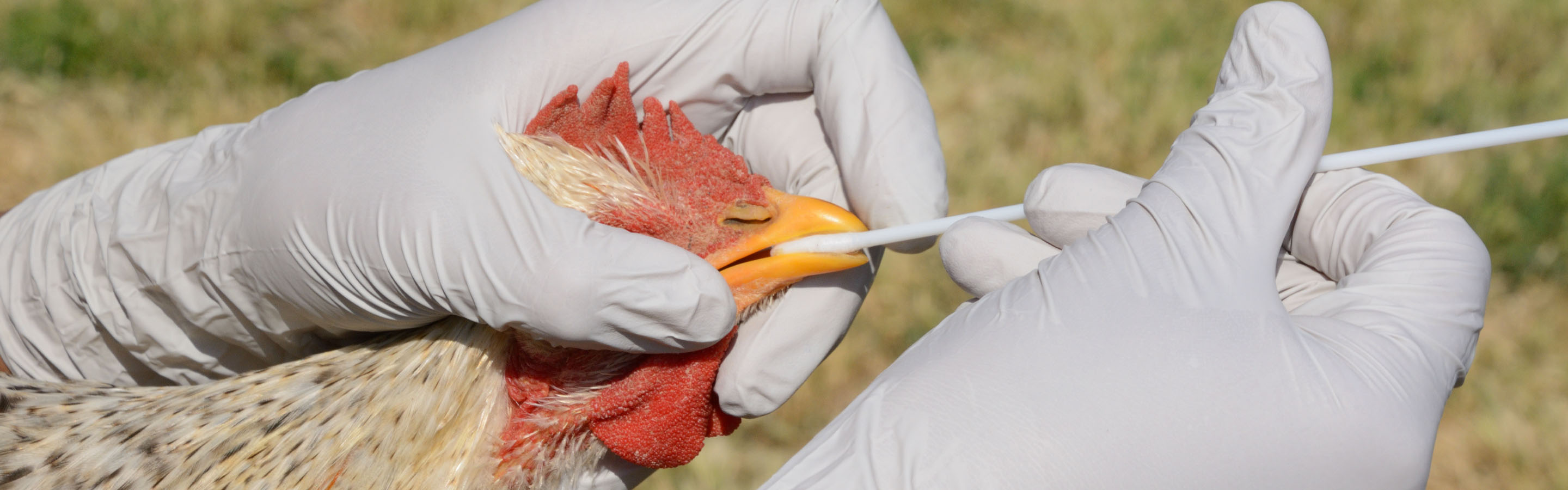
Transmission and Prevention

Avian influenza, also known as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral disease that can affect both birds and humans. Understanding how it spreads and taking preventive measures are crucial to minimize the risk of infection.
Transmission between Birds and Humans:
– Direct contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids
– Contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
– Inhalation of respiratory droplets from infected birds
Prevention for Poultry Farmers:
– Implement strict biosecurity measures to prevent contact with wild birds
– Vaccinate poultry to reduce susceptibility
– Practice good hygiene and use protective gear when handling birds
Prevention for Individuals:
– Avoid contact with sick or dead birds
– Wash hands thoroughly after handling poultry or their products
– Cook poultry products to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C)
Role of Biosecurity Protocols:
– Restricting access to poultry areas
– Disinfecting equipment and vehicles
– Monitoring bird health and reporting any suspicious signs
– Isolating infected birds and implementing quarantine measures
Impact on Poultry Industry
Avian influenza outbreaks can have severe economic consequences for the poultry industry. Production losses due to illness and mortality can lead to significant financial losses for farmers. Market disruptions, such as trade restrictions and consumer avoidance of poultry products, can further exacerbate these losses.
Strategies for Mitigating Impact, Avian influenza
To mitigate the impact of avian influenza, poultry farmers have implemented various strategies. These include:
- Enhancing biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of the virus into flocks.
- Implementing vaccination programs to reduce the severity of disease and mortality.
- Adopting alternative production systems, such as free-range or organic farming, which can reduce the risk of transmission.
Developing Resilient Systems
Developing resilient poultry production systems in the face of avian influenza is crucial. This involves:
- Investing in research and development to improve vaccines and diagnostic tools.
- Promoting collaboration between farmers, industry stakeholders, and government agencies to share information and best practices.
- Encouraging the adoption of sustainable farming practices that reduce the risk of disease outbreaks.
By implementing these strategies, the poultry industry can mitigate the impact of avian influenza and ensure the continued production of safe and affordable poultry products.
Public Health Concerns: Avian Influenza
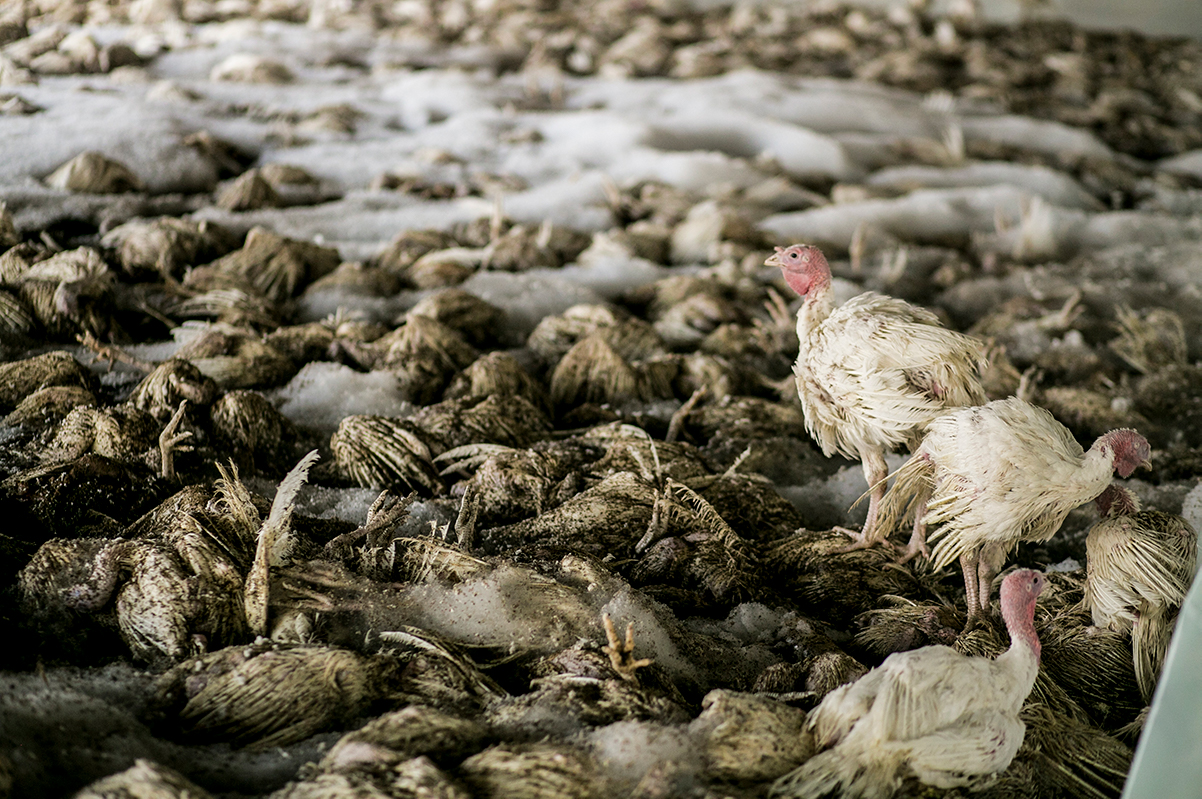

Avian influenza is not just a threat to poultry; it can also pose a risk to human health. The virus can be transmitted to humans through contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids. The most common way for humans to get infected is through exposure to infected poultry or their feces.
Symptoms of avian influenza in humans can range from mild to severe. Mild symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Severe symptoms can include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and even death.
Surveillance and Response Measures
Public health authorities are constantly monitoring for avian influenza in humans. They work with veterinary authorities to track the spread of the virus in animals and to identify any human cases. When a human case is identified, public health authorities will investigate the case and try to identify the source of the infection. They will also work to prevent the spread of the virus to other people.
Collaboration Between Veterinary and Public Health Sectors
Collaboration between veterinary and public health sectors is essential for managing the public health risks associated with avian influenza. Veterinary authorities are responsible for monitoring the spread of the virus in animals and for implementing measures to control the virus. Public health authorities are responsible for monitoring the spread of the virus in humans and for implementing measures to prevent the spread of the virus to other people.
By working together, veterinary and public health authorities can help to protect human health from avian influenza.
Avian influenza has been making headlines lately, and it’s a serious issue. The virus can spread quickly through poultry flocks, and it can even be deadly to humans. But fear not, for there is hope! A promising young footballer named Miguel Borja has emerged as a potential savior.
His skills on the pitch are said to be unmatched, and his determination to overcome any obstacle is an inspiration to us all. Just like the virus, Borja is spreading quickly, but instead of causing harm, he’s bringing joy and hope to the world of football.
And just as we can fight back against avian influenza, we can also support Borja and his team as they strive for greatness.
Guys, I’ve got some serious news for you. Avian influenza is no joke, but hey, let’s not dwell on that right now. Instead, let’s talk about something more exciting – who won the Home Run Derby 2024? I know, I know, it’s a bit random, but I’m curious.
If you want to find out, click here. Now, back to avian influenza. It’s still a big deal, so let’s stay vigilant, folks.